
Hematology
Advertisement
Oral avatrombopag shows promise in kids with ITP, offering a safer, effective alternative to current treatments.
Researchers also measured in the study cohort a very high discontinuation rate for this agent.
In a cohort of adults and adolescents marstacimab produced bleed control superior to that from on-demand bypassing agent.
The agent notably in preclinical studies has accomplished increased HbF without any evident cytotoxicity.
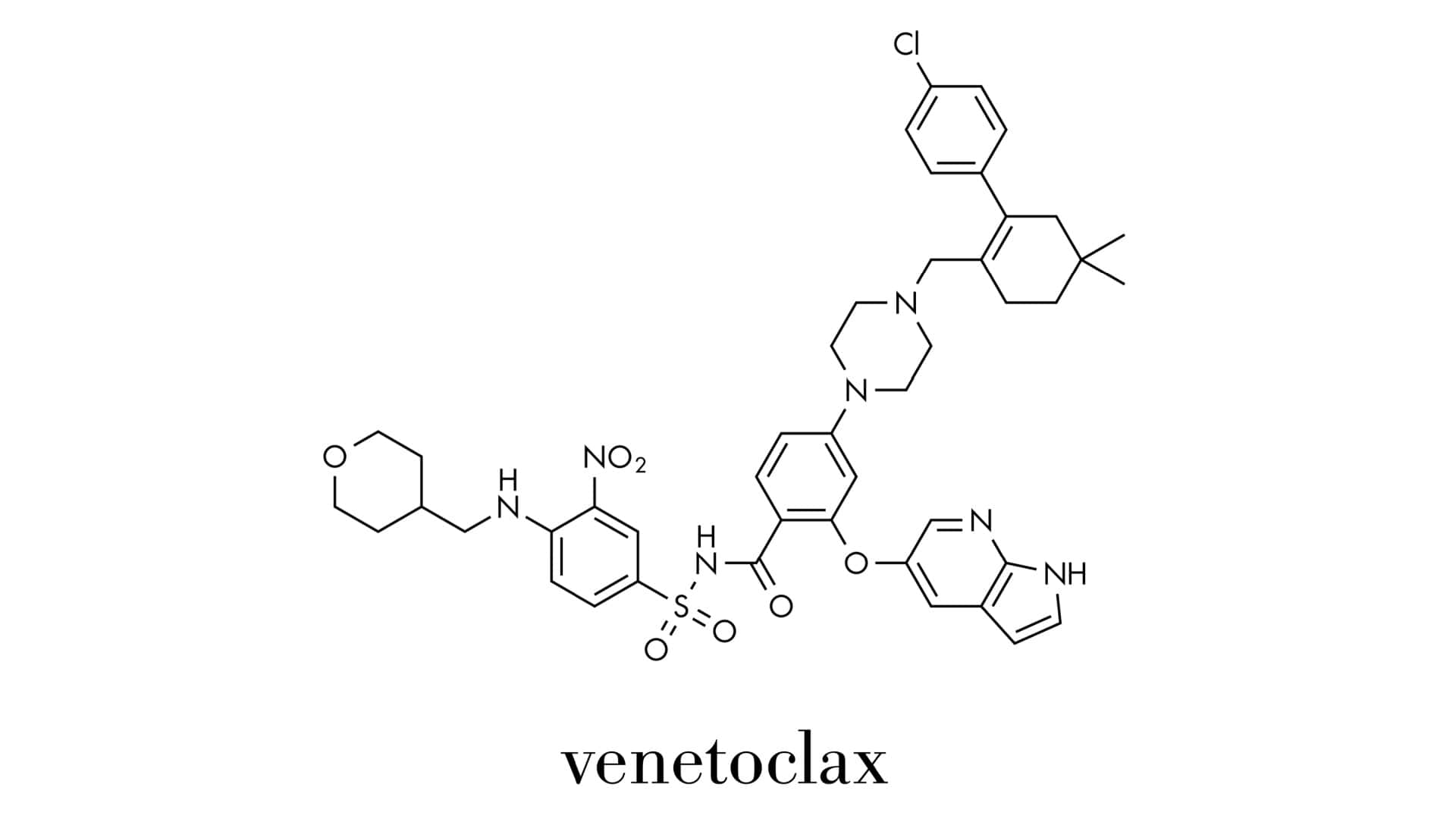
The phase 3 VERONA trial, which compared this combination with placebo plus azacitidine, observed no new safety signals.
Dr. John Gansner and Dr. Martina H. Slingsby argue this new agent can provide benefit across all bleeding disorders.
Heme Today spoke with Ulrike Reiss, MD, and Andrew Davidoff, MD, of the trial's investigator team.
Gene therapy is reshaping sickle cell care, raising awareness and advancing treatments beyond the lab.
ASH warns NIH cuts would jeopardize blood disorder care and halt key progress in hematology research.
Reduced-intensity HSCT conditioning with lentiviral gene therapy decreased severe vaso-occlusive events by more than 80%.
An interim analysis of the COMPLETE study found that pegcetacoplan improved indicators of blood health.
The SURPASS ET trial evaluated efficacy and safety of ropeginterferon alfa-2b in second-line ET treatment.
Data were presented at EHA2025 on the novel anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody CM313 for chronic ITP.
Evidence was presented at EHA2025 that the agent improves RBC health and blood flow in patients.
Two cases of patients with SCD and history of delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction were presented at EHA2025.
The analysis was an assessment of 15-year follow-up data from the CLIMB study and was presented at EHA2025.
The study data presented at EHA2025 were from patients who had disease resistant to prior therapy or intolerance to therapy.
The FDA previously granted Orphan Drug Designation to nuvisertib for use in myelofibrosis in May 2022.
Vivien Sheehan, MD, explained how a novel assay can guide personalized therapeutic approaches for sickle cell disease.
Rilzabrutinib significantly decreased spleen weight and reduced inflammation in mice with homozygous sickle cell genotype.
Advertisement












 © 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.
© 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.