
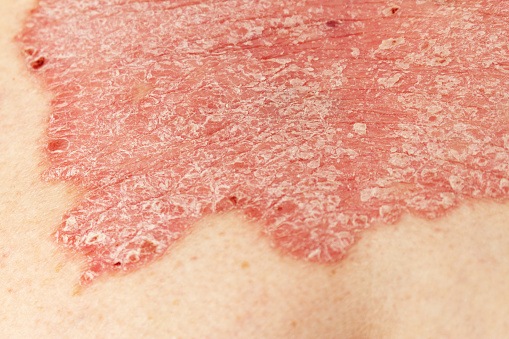
Risankizumab is a humanized monoclonal interleukin-23 antagonist antibody used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). and erythrodermic psoriasis (EP). In a recent paper published in Clinical Pharmacokinetics, the study researchers assessed relationships between risankizumab exposures and crucial efficacy and safety variables in a cohort of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, GPP, or EP after being treated with 75 or 150 mg subcutaneous doses at weeks zero and four and every 12 weeks subsequently.
The study authors correlated risankizumab average plasma concentrations with probabilities of achieving the primary efficacy endpoints, which were Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75, PASI 90, PASI 100, and Static Physicians Global Assessment (sPGA) 0/1. Data were evaluated on Japanese (n = 225) and non-Japanese (n = 1,678) moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis patients participating in global trials or a Japan Phase 2/3 trial.
In the Japanese patient cohort, the exposure-efficacy relationships were comparable with those of patients in global Phase 3 trials. The researchers reported a 16-week efficacy plateau for 150 mg subcutaneous dose; the PASI 90 response probability was 77%, while the sPGA 0/1 response probability was 88%. Exposures were not as great in heavier patients for the 75 mg dose for PASI 100 response and other efficacy responses. No correlation between risankizumab average plasma concentrations and key safety variables (any adverse event, serious adverse event, infection and infestation, and serious infection during treatment) were observed in exposure-safety analyses—this was similar to results from global trials.
The study authors concluded that risankizumab 150 mg was efficient in treating Japanese psoriasis patients and posed no significant safety concerns.






 © 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.
© 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.